What's New in Revit 2025

Autodesk Revit, the most used building design and documentation software, has released the much-expected 2025 version with some new features and improvements. This version contains the new Total carbon analysis with Insight, sheet collections feature, substantial Toposolid enhancements, support for .NET Core 8, and many improvements.
Table of Contents
- 1 - Relevant for Everyone
- 2 - Relevant for Architects
- 3 – Relevant for Structural Engineers
- 4 – Relevant for MEP Engineers
- 5 - Relevant for Advanced Users and BIM Managers
- 6 - Relevant for Programmers
- Last words
Revit 2025 is released!
As a Revit enthusiast, you might find it interesting to note that Autodesk's release of Revit 2025 is now available globally. In our view, this update is categorized as a minor release, especially when compared to the major overhaul experienced with Revit 2024, which introduced significant changes including new icons and a new Dark mode. While Revit 2025 does roll out new features, they do not carry the same weight or impact as those seen in the previous version. Nevertheless, these enhancements are designed to refine your workflow, bringing about improvements that, although subtle, are aimed at making your daily tasks more efficient and enjoyable.
One of the most significant improvements in Revit 2025 in our opinion is the new Total carbon analysis with Insight and forma.
The user feedback and requests seem to be the main driver of this new release, resulting in enhancements in the Toposolids realm, including excavation, volume calculation, support for shaft openings, and enhanced visualization. The Toposolids feature released in Revit 2024 was one of the most criticized tools, with many users skeptical of its workflow and results. Are the new improvements sufficient to calm down those users?
The native tool for PDF export will allow you to publish PDFS in the background while you are doing your work. Revit 2025 has also taken collaboration to the next level, making working with others across different disciplines more accessible than ever.
There are also improvements for the stuctural and MEP engineers, including the support of a gbXML 7.3, and Autodesk claims that Revit installs 20% faster in this last release.
So, let's go through all the Revit 2025 new improvements and features:
1 - Relevant for Everyone
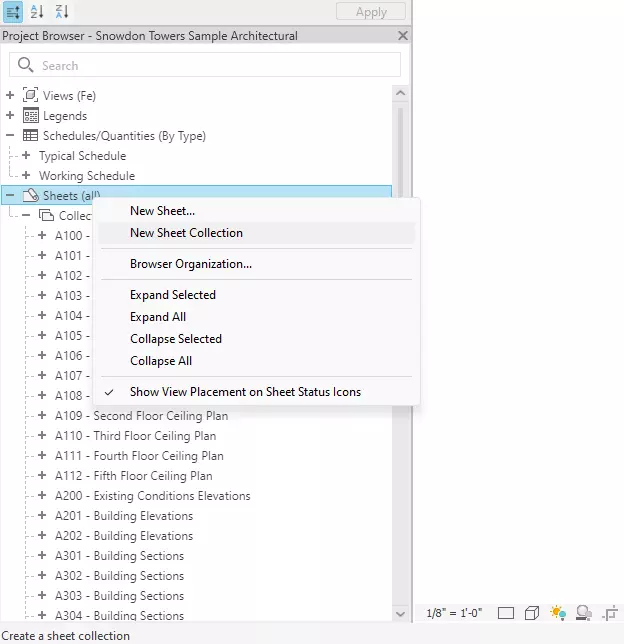
1.1 - Sheet Collections
This is a new top level structure that allows to organize sheets into folders. This new feature will allow for instance to use the same sheet number in the same project. Maybe benefitial for some users, hence this new feature, but we are somehow skeptical to it.
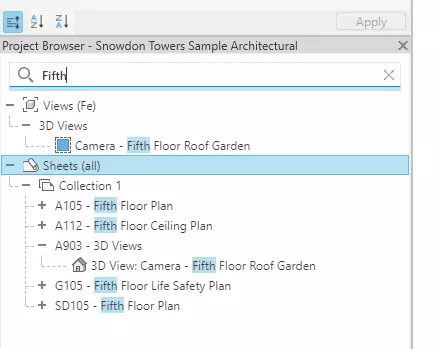
1.2 - Search in Project Browser Enhancement
Revit 2025's Project Browser now comes with an enhanced search functionality, making it simpler for professionals to navigate through a project's complex hierarchy. This upgrade ensures that when you search for a term, all related elements are displayed, including child nodes under parent nodes containing the keyword. This not only streamlines the search process but also aids in maintaining an organized view of the project components. Such advancements in the software's usability demonstrate a commitment to improving the user experience for architects and designers.
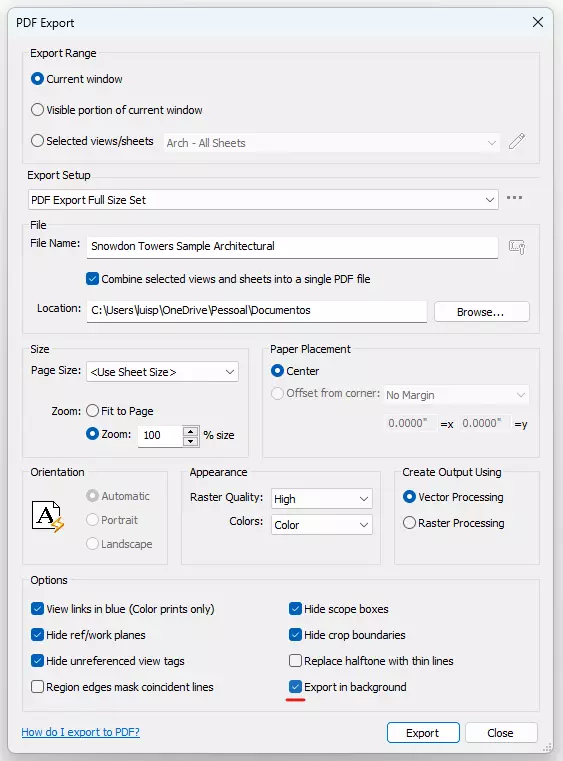
1.3 - Background PDF Export
Autodesk has been listening to the pain of many users that have call a Publishing day, when large projects were exported into PDF and the user could not do anything else in the Revit session. So now it is possible to Publish as a background operation.
1.4 - Option Bar Removal
Revit 2025 will no longer have the option bar that was located directly under the ribbon bar. Instead its settings are placed in the properties.
1.5 - Improved Vector Processing
The feature highlighted here improves vector processing when printing to PDF or exporting to CAD formats. Specifically, it enhances the output of views with transparent and overlapping elements, aiming to closely match the on-screen appearance of such elements in the final output. This improvement leads to more consistent representations of model and detail elements in prints, PDFs, and DWG exports, ensuring transparency and overlapping is handled effectively. It enhances the clarity and quality of documentation, making it more reliable and visually accurate for professionals relying on these exported formats for presentation or collaboration.
1.6 - Next Generation Insight: Total Carbon Analysis
Autodesk's launch of Total Carbon Analysis for the AECO sector is a progressive move aimed at tackling the high carbon footprint associated with the built environment. This novel feature within the Autodesk AEC Collection arms architects with real-time carbon analysis tools, from the onset of planning through to the finer details of design. It promotes intelligent decision-making with AI-enhanced tools like Embodied Carbon Analysis in Forma and extends capabilities within Revit and Autodesk Insight. These tools allow professionals to meticulously assess and optimize their designs for lighting, HVAC, and material selection, driving down the carbon impact. By integrating these advanced features, Autodesk is enabling architects to access comprehensive carbon data, facilitating informed decisions that balance embodied and operational carbon. The goal is to nurture a culture of sustainability that not only meets but surpasses green building standards, reflecting Autodesk's commitment to environmental stewardship in design and construction.
2 - Relevant for Architects
2.1 - Toposolid Improvements
Users who have worked extensively with Revit's 2024 version have noted that toposolids weren't quite up to par with their expectations, often citing them as underdeveloped for professional needs. The feedback suggests that the initial release of toposolids lacked some functionality that would allow for complex, precise site modeling workflows. Autodesk appears to be responding to this feedback by enhancing the toposolid toolset in Revit 2025, but such development takes time as it involves refining algorithms, ensuring compatibility with existing features, and rigorous testing to meet the high standards required for architectural software. These iterative improvements are part of Autodesk's ongoing commitment to address user feedback and evolve the capabilities of Revit. Autodesk has dedicated quite a bit of effort on improving the toposolids, making this the most relevant change for architects. Lets have a look on what are the improvements:
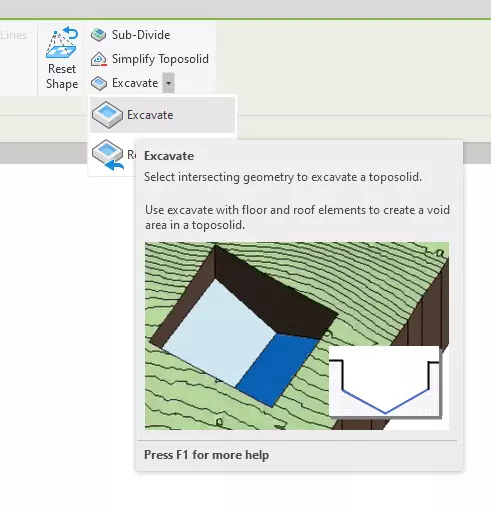
2.1.1 – Excavate on Toposolid
Revit 2025 introduces a significant feature for site modeling: the ability to excavate toposolids using architectural elements. Now, designers can directly use elements such as floors, roofs, and toposolids to create excavations, eliminating the extra steps previously required. This enhancement mirrors real-world site preparation, where the building's structural elements themselves dictate the excavation parameters. This upgrade simplifies the process of integrating structures with the landscape, enhancing the software's utility for site development tasks.
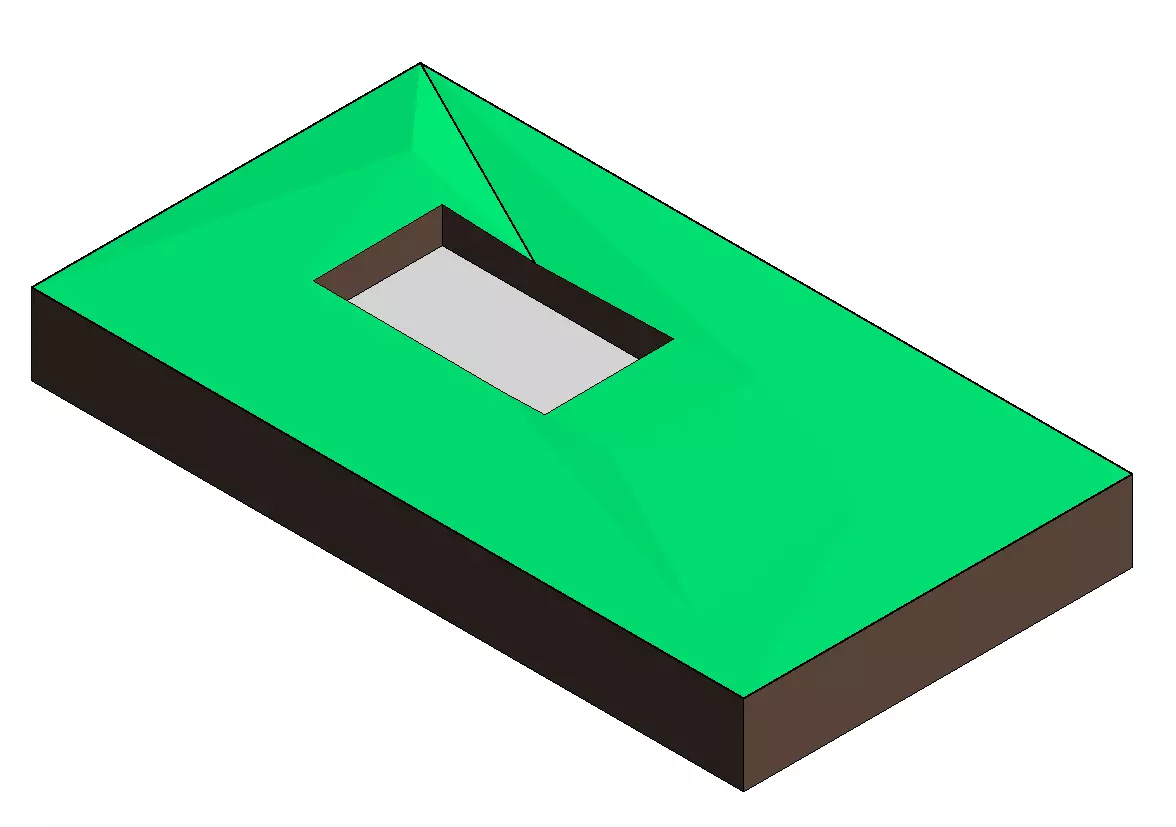
2.1.2 – Model by face Toposolid
Revit 2025 enhances the functionality for users who utilize massing by enabling the creation of toposolids from mass faces. This feature, accessible from the Massing & Site tab, streamlines the process, allowing more intricate modeling of terrain or other forms directly from massing geometry. With the "Model by Face" tool, you can now select a face of a massing element to generate a toposolid, which automatically includes contour lines, offering another workflow for modeling site elements and other complex forms in Revit.
2.1.3 - Excavation Volume Parameter for Boolean Objects on Toposolid
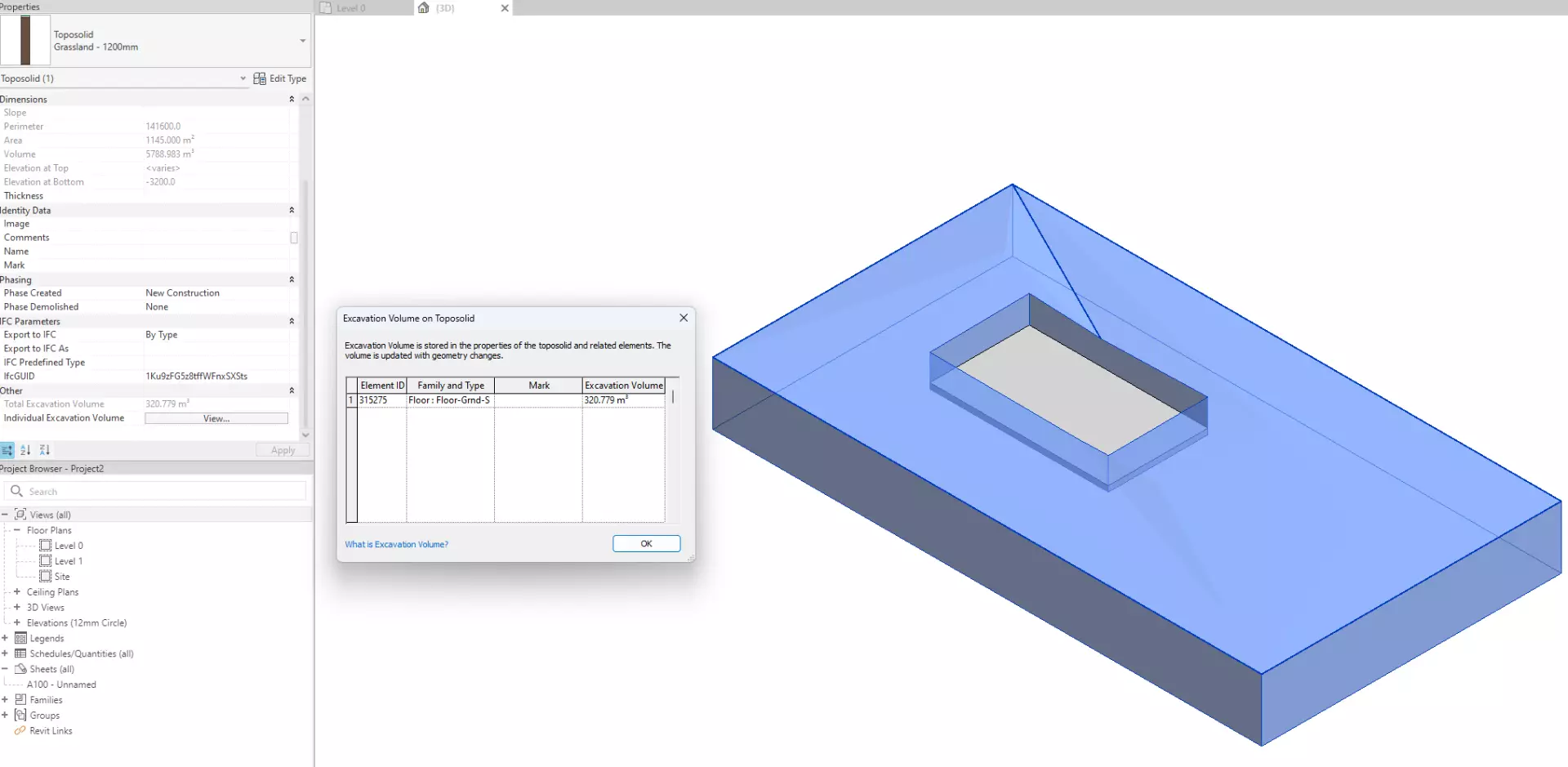
Now the Cutter Elements that performed the Cut/Join/Excavate with Toposolid, will show the Excavation Volume on Toposolid Parameter. Including all the categories that can do Boolean operations on Toposolid (Wall, Floor, Building Pad, Mass, Component-in-Place, etc.)
2.1.4 – Smooth Toposolids
The Toposolid Smooth Shading feature in Revit 2025 brings a more refined visual experience to the modeling of terrain elements. With this feature activated, users can enjoy a more natural and smoother appearance of toposolids in 3D views, enhancing visual presentations and renderings. This doesn't alter the actual geometry of the toposolids, it's purely for visual enhancement. To enable this, users can navigate to the Massing & Site tab and select the Toposolid Smooth Shading option, providing an immediate improvement to the display quality of their toposolid elements within their Revit models.
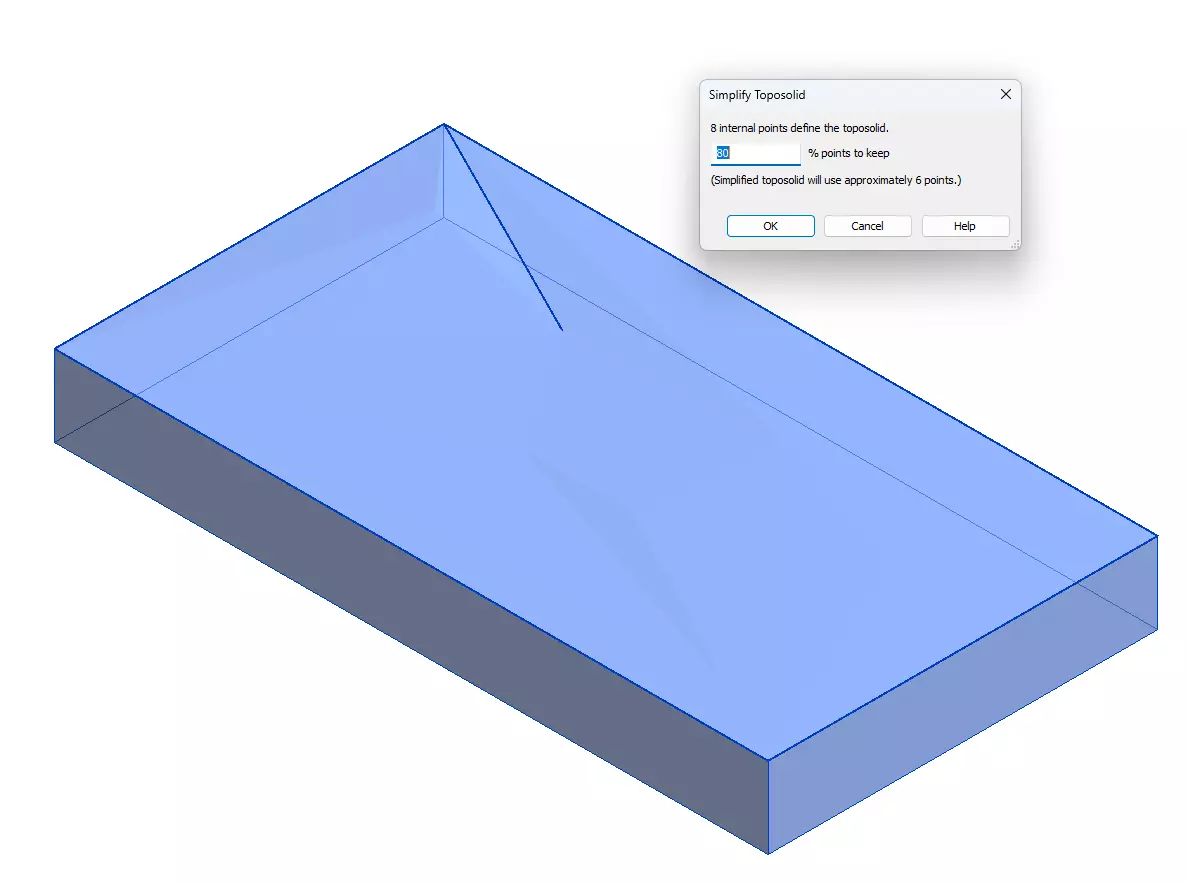
2.1.5 – Simplify Toposolid
Users can adjust the Point number by inputting the percentage that they want to preserve.
2.1.6 - Shaft Opening Ennhancement
Now the ShaftOpening will respond to Toposolid Bottom constraint to not cut through the earth.
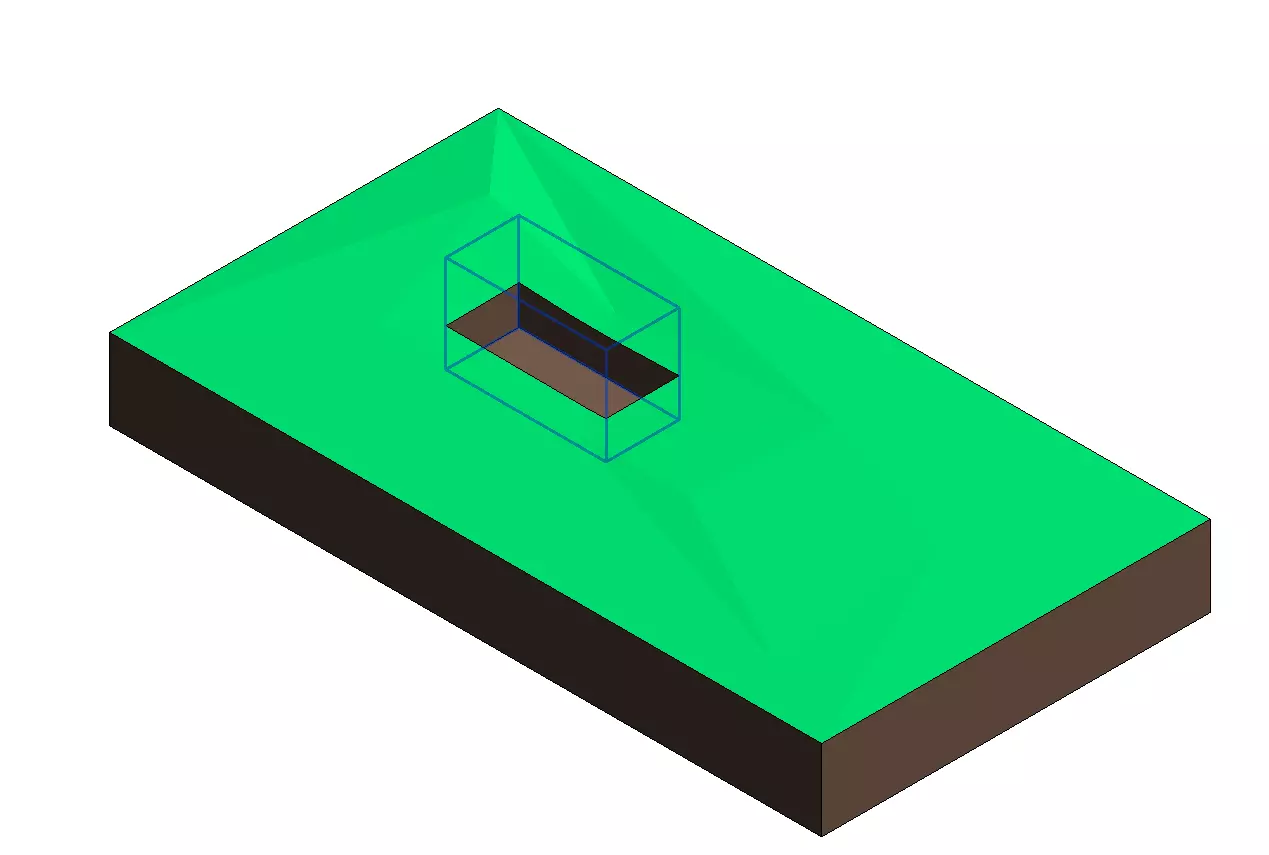
2.1.7 - Toposurface Conversion Improvement
The feature enhancement allows you to convert a topographic surface (toposurface) to a volume (toposolid) while now including building pads within the conversion process. In previous version of Revit, when converting toposurfaces to toposolids, the building pads were omitted, but with Revit 2025, they are recognized and incorporated, allowing for a more integrated and complete representation of the terrain and the built environment elements within a project model. This improvement aids in maintaining continuity and reducing the need for workarounds when upgrading older project files to Revit 2025.
2.2 - Align Multiple Annotations
Now the text annotations can be easily aligned and distributed.
2.3 Room Perimeter Accuracy Improvement
Previously Revit did not consider the inner loops of a room. With Revit 2025 the perimeter will quantify all the room loops. The perimeter calculations on upgraded projects will be automatically upgraded to this rule.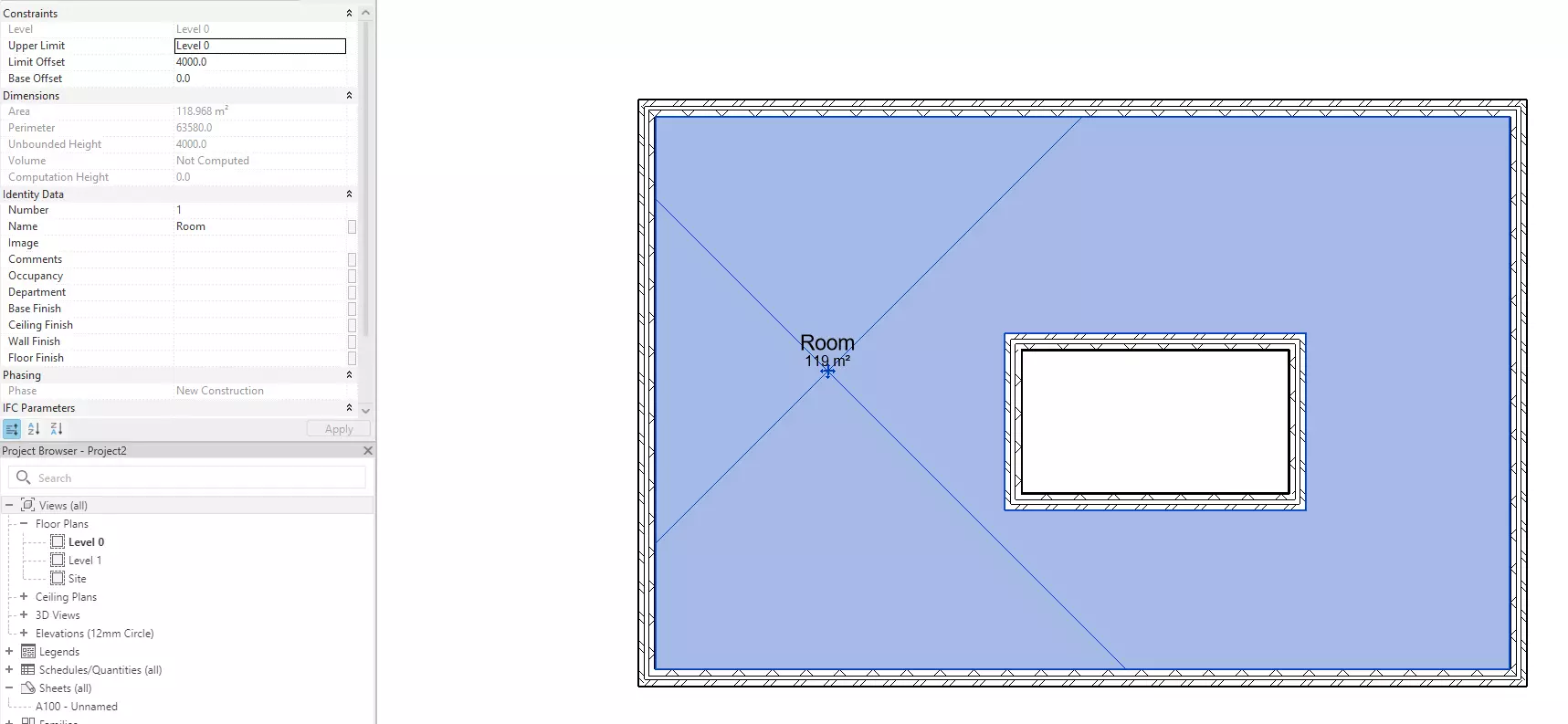
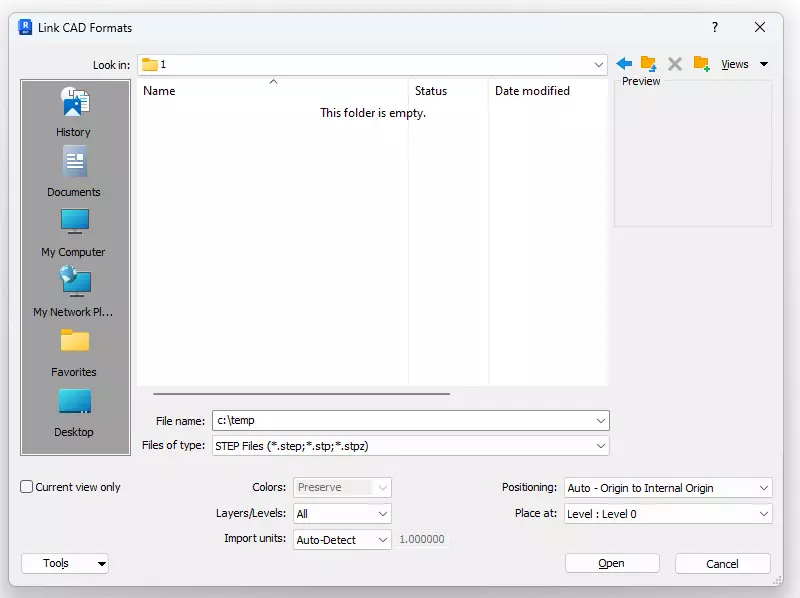
2.4 - STEP File Import, Export, Link
The new feature for importing and exporting STEP files in Revit 2025 has been introduced to provide extended support for working with CAD files. Users can now directly import/link STEP files, including .step, .stp, and .stpz formats, into their Revit models. This improves the interoperability between different software used in design processes. Additionally, there is an option to export STEP files from 3D views of your Revit models, allowing for easier sharing and collaboration across different platforms. Users can also save their export setups for future use, streamlining the workflow for subsequent exports. For a detailed explanation and guidelines, users can refer to the Export to SAT/STEP section within the Revit documentation.
2.5 - Auto Join and Lock When Placing Walls
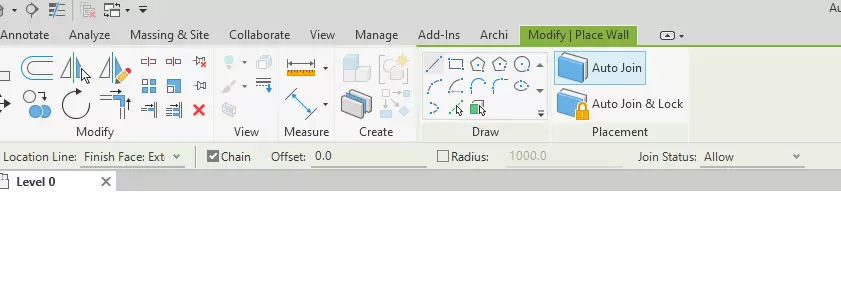
The new feature in Revit 2025 greatly streamlines the process of creating and managing walls in architectural models. When placing walls, users can now automatically join a new wall with an adjacent one using the "Auto Join" feature, or use "Auto Join & Lock" to join and simultaneously lock the walls, speeding up modeling workflows and ensuring consistency. However, these features are restricted to certain types of walls and do not apply to stacked walls, curtain walls, or walls with certain geometries like slanted or tapered walls. This improvement is aimed at enhancing productivity by simplifying the steps required to refine the model's structure.
2.6 - Material Thumbnail Generator Improvement
This simple upgrade will ensure that the material thumbnails will generate quicker.
2.7 - Multiple Loop Mullion Profiles
Revit 2025 introduces a significant enhancement to mullion profiles for curtain walls, where mullions can now incorporate multiple loops within their profiles. These loops can either be internal, carving out sections within the mullion profile for more detailed geometry, or external, adding more complex forms to the mullion's silhouette. The illustration and text demonstrate that such multi-loop profiles allow for greater detail and intricacy in curtain wall designs, closely simulating real-life conditions and construction details, albeit without the ability to assign different materials to individual parts of the mullion. This new feature opens up possibilities for more sophisticated façade designs directly within the Revit environment.
2.8 - Disable/Enable Wall End Wrappings in Canvas
The new In-Canvas Wall Wrapping Control in Revit 2025 enhances the ability to manage wall end conditions. This feature allows users to adjust how wall layers wrap at the ends directly within the plan view, providing a visual and intuitive interface to customize wall joins without needing to delve into wall structure settings. It simplifies the process of achieving accurate wall joins and representations, ensuring that the visual model closely aligns with the intended construction details.
3 – Relevant for Structural Engineers
3.1 - Revit Robot Structural Analysis Interoperability Updates
3.2 - Parametric Splicing for Typical Rebar
The "Parametric Splicing for Typical Rebar" feature in Revit 2025 introduces advanced capabilities for modeling rebar splices within a 3D structural model. This feature allows users to define the location of splices within rebar sets, control the lap length, and choose between uniform or staggered layouts, ensuring adherence to engineering and fabrication standards.
Parametric splicing essentially means that the splice locations and lengths can be determined based on parameters or rules, which can be predefined or adjusted as needed. This provides flexibility in the detailing process and ensures that changes to the model or design specifications can be rapidly implemented across the project.
Users can splice rebar sets by selecting the appropriate set or a reference line directly in the model, whether they're working in 2D or 3D views. They can define maximum and minimum lengths for the rebars, as well as specify the run-out positions, which is the part of the rebar extending beyond the end of the splice. Additionally, the feature allows users to simultaneously change properties of multiple splices between rebar sets, facilitating efficient updates and ensuring consistency across the model.
This functionality is particularly important for the accurate detailing and visualization of reinforcement in concrete structures, aiding in the planning of construction phases and the preparation of rebar for fabrication. It streamlines the process of rebar detailing, making it more efficient and less prone to errors.
3.3 - Highlight Bars Exceeding the Maximum Length
The "Highlight Bars Exceeding the Maximum Length" feature in Revit 2025 offers a streamlined approach to ensuring rebar elements within a model comply with specified length requirements. By visually distinguishing rebars that exceed the maximum permissible length, highlighted in vivid red, users can quickly identify and address potential issues in their structural design. This visual cue simplifies the review process, making it more efficient to verify and adjust rebar lengths according to the project's standards. Furthermore, the feature allows for customization through view filters, enabling users to set and apply their own criteria for minimum and maximum lengths, thus tailoring the inspection process to the specific needs of each project.
3.4 - Prevent Unexpected Changes to the Rebar Model
The "Prevent Unexpected Changes to the Rebar Model" feature in Revit 2025 is designed to maintain the integrity of a rebar design within a concrete structure model. It allows users to disable rebar constraints for individual bars or entire rebar sets, effectively locking their geometry to prevent automatic adjustments when changes occur in the concrete host geometry. This ensures that the specified positioning and detailing of the rebar elements are maintained throughout the design and revision processes.
For instance, if the dimensions of a concrete beam or column are altered, any rebars with constraints disabled would not automatically adjust to these changes. This is beneficial when certain rebar placements are finalized and should not be modified, even if the surrounding concrete geometry is.
The feature likely includes an interface where constraints can be toggled on and off with ease. It also appears to allow for manual dragging of rebar handles with constraints disabled, offering precise control over adjustments when necessary. Additionally, the use of schedules and filters to monitor the status of rebar constraints would aid users in managing the complex configurations of rebar within a model, ensuring that all elements are accounted for and properly set according to project specifications.
3.5 - Schematic Bar Bending Details for Rebar Tagging
The "Schematic Bending Details for Rebar Tagging" feature introduced in Revit 2025 is a detailed visual aid for conveying rebar bending instructions within the modeling environment. It enhances the representation of rebar layouts by embedding tags that show bending details directly in the model. This allows for a more informative and interpretable depiction of how each rebar element should be fabricated and placed.
The feature enables users to add schematic bending details that reference specific rebar elements, providing clarity on the bending shape required. With the ability to edit the visibility and appearance of multiple leaders for schematic bending details, users can customize how the information is displayed to better fit the project’s documentation standards. Users can also specify the width and height of the schematic bending details in the type properties, allowing for adjustments in the level of detail and scaling to fit different project scales.
Schematic bending details resemble bending schedules in the way that they scale the geometry of rebar shapes, adjusting the depiction based on the angle of bends, and are particularly useful for clearly showing rebar with standard 90-degree bends as well as those with non-standard angles. This feature streamlines communication between the design team and the construction personnel, ensuring that the rebar is fabricated precisely to the project's specifications.
3.6 - "Split" Features Enabled for Framing and Columns with Steel Connections
The "Split Features for Framing and Columns with Steel Connections" in Revit 2025 introduces new functionalities to handle the segmentation of steel structures. It includes two tools: 'split' and 'split with gap', which can be applied to steel framing and columns that have connections. This enhancement aims to give engineers and designers precise control over steel elements and their connections.
The 'split' tool allows users to divide steel members into separate parts, while the 'split with gap' tool goes further by introducing a specified gap between the divided sections. The gap can vary between 1.6mm to 304.8mm, accommodating different design and construction needs, such as for thermal expansion, construction tolerances, or to simply illustrate a detail in the design phase.
However, the 'split with gap' tool is not applicable to beams that are part of a beam system, truss, or a group, which may be due to the complexity or the interdependencies of these systems that could complicate the introduction of a gap. This feature is crucial for the detailed modeling phase of structural design, ensuring that the steelwork is accurately represented and can be understood and constructed correctly by the construction teams.
3.7 - Transfer Advance Steel Part and Assembly Marks to Revit
The "Use Advance Steel Part and Assembly Marks in Revit" feature in the 2025 update is geared towards enhancing interoperability between Revit and Advance Steel. It enables users to create general arrangement drawings for steel projects in Revit that are more closely integrated with the detailing processes in Advance Steel. This is accomplished by importing part and assembly marks from Advance Steel into Revit.
This integration ensures that the identification marks for parts and assemblies used in Advance Steel, which are crucial for the fabrication and assembly of steel structures, are consistent and accurate in the Revit model. This consistency is critical across design, fabrication, and construction stages, as it allows for clear communication and efficient coordination between different teams working on the project.
With this feature, users can transfer the detailed numbering and marking systems of steel components from Advance Steel into Revit. These marks are essential for tracking individual parts and their respective positions in the overall steel assembly. This could include the placement of bolts, plates, and other connections within a steel structure, facilitating the generation of accurate and informative construction documents directly from the Revit model.
4 – Relevant for MEP Engineers
4.1 - Latest Version gbXML (v.7.03)
The gbXML v7.03 update brings a comprehensive set of enhancements to support sophisticated energy and environmental modeling in Revit. It introduces new elements for HVAC design like chillers, cooling and heating coil types, and adds numerous system definitions for air and hydronic loops. With additional enumerations for equipment and constructions, along with more robust analysis parameters, this version allows for more detailed modeling of thermal systems, their components, and their performance. Revit's support for this advanced version underpins its commitment to detailed, accurate sustainability studies in building designs.
4.2 - More Easily Access Duct & Pipe Pressure Drop Data
4.3 - Single-phase Components within Three-phase Power Distribution Systems
The new feature for Revit 2025, "Single Phase Electrical Components," enhances the software's electrical modeling capabilities by introducing support for single-phase electrical systems. This addition allows for a more accurate representation of electrical loads and distribution systems commonly found in residential and light commercial projects. With this feature, engineers and designers can now incorporate single-phase components into both analytical and physical models, improving the precision of electrical simulations and documentation for projects that utilize single-phase power.
4.4 - More Accurate Energy Analysis in Annual Operating Schedules
The enhanced operating schedules in Revit 2025 can mirror the unique operational dynamics of various building types more accurately. For example, schools often have distinct schedules with clear-cut holidays, seasonal breaks, and varied weekday and weekend usage patterns. Office buildings might operate primarily on weekdays, with different occupancy and energy use profiles for weekends or off-hours. Hospitals, which operate 24/7, might still have varied energy usage patterns based on shifts in staff and patient activity. By allowing for the specification of these varying conditions within a model, Revit can assist in creating more realistic energy models that reflect actual energy consumption, leading to more precise sustainability and efficiency assessments. This feature significantly bridges the gap between simulated building performance and real-world operation.
5 - Relevant for Advanced Users and BIM Managers
5.1 - Array of 1 or 0 in Families
Revit 2025 introduces the capability for designers to create families with arrays that can have a count of 0 or 1, expanding the flexibility and control within the Family Editor. Previously, array counts could not go below 2, which could be limiting in design scenarios. With this new update, manufacturers and design firms that work extensively with Revit families can significantly reduce the time and effort required for family maintenance and offer improved compatibility. For example, furniture arrays can be adjusted to show no chairs by setting the array count to 0, while still keeping the table visible in the model. This refinement means some older family content may need to be updated to harness these new array capabilities. However, it's important to note that this feature is exclusive to the Family Editor and does not apply to project-level array creation.
5.2 - Batch Delete and Add to Material Library
5.3 - Improved IFC Export Category Mapping Table
The IFC Export Category Mapping Templates feature in Revit 2025 allows for customization of category mapping for IFC file exports. This means that users can now more precisely control how Revit categories are defined within the IFC data structure. This is beneficial for ensuring data integrity during collaboration and exchange of BIM models across different software that supports the IFC standard. The mapping settings created can be saved as templates and used across multiple Revit models, streamlining the process for future exports and maintaining consistency in data exchange. For more in-depth usage, one would refer to the 'Manage IFC Export Mapping Settings' section in the Revit documentation.
6 - Relevant for Programmers
6.1 - NET8.0 Updates
Revit is primarily built using C++, a powerful programming language that provides performance and low-level memory control. However, Revit also includes a .NET API that allows for additional programming using .NET compliant languages, including Visual Basic.NET, C#, and C++/CLI. The .NET API is particularly used for developing custom plugins and extensions, giving developers the ability to automate tasks and extend Revit's core functionalities.
With the introduction of .NET 8 in Revit 2025, the software's API layer now supports the latest .NET Core features, which includes performance improvements and other enhancements like advanced JIT (Just-In-Time) compilation and improved garbage collection. This move aims to leverage the speed and efficiency improvements of .NET Core while ensuring compatibility and a more robust platform for plugin developers. However, this upgrade does mean that developers who maintain plugins and extensions for Revit may need to update their code to be compatible with the newer .NET version, ensuring their products can benefit from these improvements. This change signifies Autodesk's commitment to keeping Revit on the cutting-edge of technology and providing a seamless experience for both users and developers.
6.2 - Dynamo Updates
Support for the latest version of Dynamo, and nodes for toposolids generation
6.3 – New Macro environment
The Macro environment has suffered some major changes. You will no longer be able to code in Python and vb net. But you will be able to code in C# using visual studio code. The macros will not be any longer document hosted. That is in my opinion something negative, as in many projects we have runed operations when the document opened and closed.
Last Words
The release of Revit 2025, while not as feature-rich as its predecessor, delivers targeted enhancements aimed at improving the daily workflows of its users. The spotlight for this year's updates shines on refinements rather than major overhauls, with a significant focus on user-driven feedback to polish existing tools.
Despite the excitement surrounding the public roadmap's projected new features, like the Next-Generation Viewport System, 3D wall capabilities, and issue tracking in connection with Autodesk Construction Cloud, these innovations are reserved for future versions. As we await the more transformative updates hinted for Revit 2026, we acknowledge the essential steps taken in Revit 2025 to ensure a solid foundation for these forthcoming advancements.
In looking forward, we anticipate that Autodesk will leverage user input and evolving technology trends to introduce more substantial updates in the next release. The expectation is that Revit 2026 will bring fresh, robust features that enhance the software's efficiency and maintain its reputation as a cornerstone in the architectural design industry.



